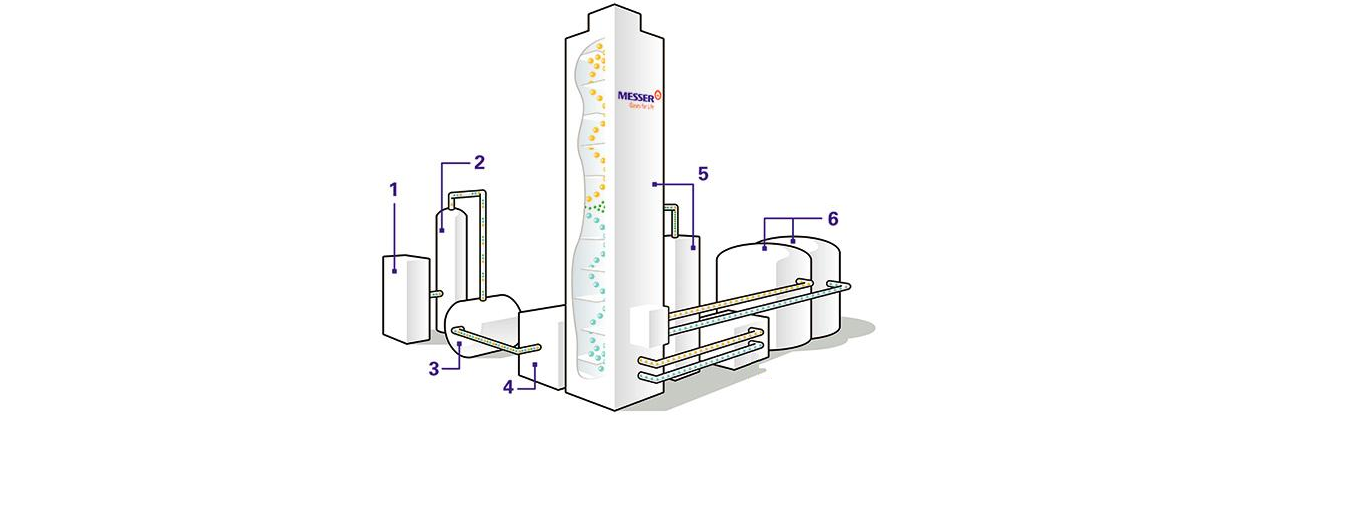
Working principle - Strategic application technology
Breadcrumb
Customer segment oil & gas refering
OIL AND GAS REFINING
Improve productivity & get more ecological processes with gases
Oil and Gas Refining
Oil and Gas Refining
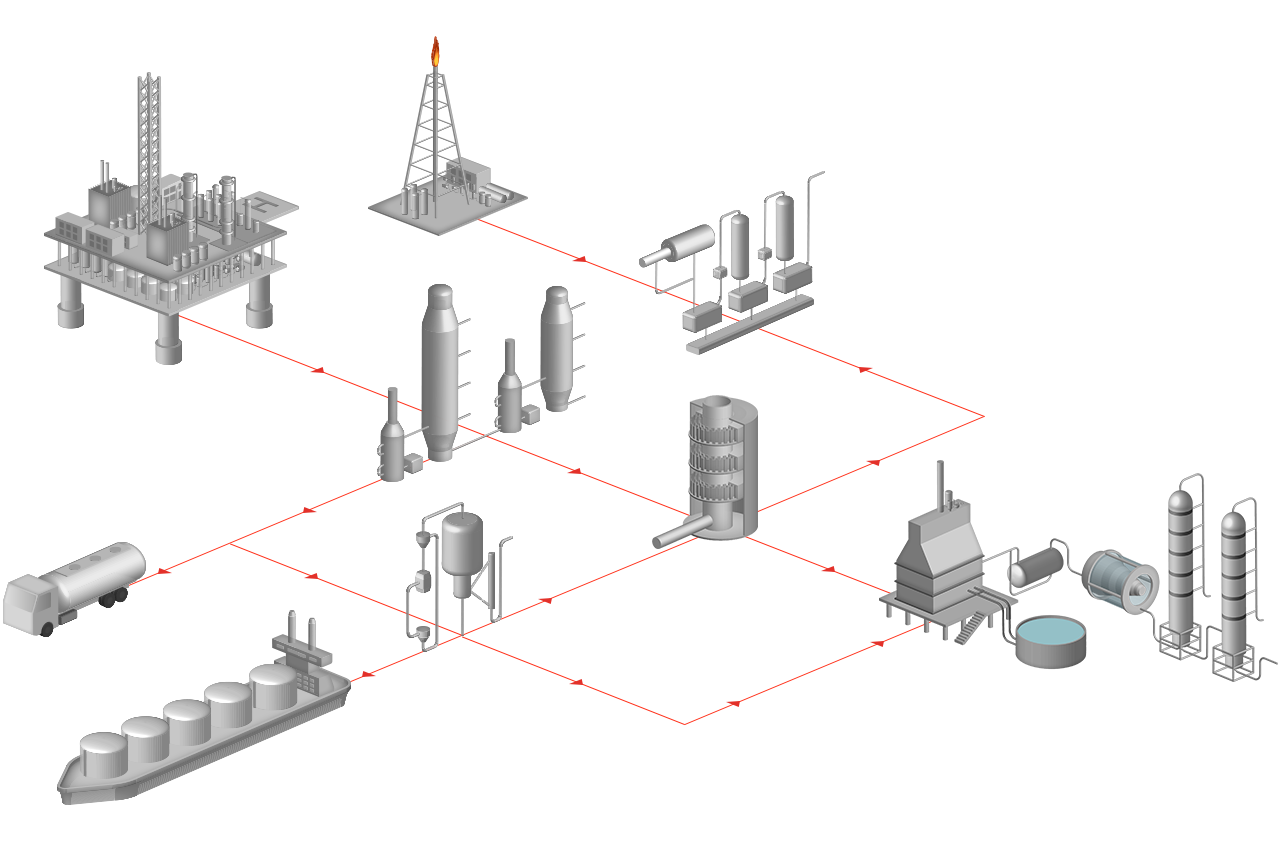
By definition, crude oil and natural gas are the raw materials of the petrochemical industry, with inert gases such as N2 and CO2 already used on a large-scale during their extraction. The processing of crude oil to the desired end products involves several steps. Again, gases from Messer are used in many of these process steps.
Customer process for oil and gas refining



Fluid catalytic cracking FCC
Major material conversion process in the oil processing industry






Leaflet
Asset Publisher
Dr. Nina
van Gellecom
Manager Chemical applications
Joachim
Rohovec
Senior Manager Chemical & Environmental applications
Other interesting topcis







Cracking of persistent COD with ozone
Equipment, expertise and gas for a complete solution



Contact
Dr. Nina
van Gellecom
Manager Chemical applications
Asset Publisher
Working principle
Application technology startpage
GAS APPLICATION TECHNOLOGIES
Productivity increase, production throughput and ecological improvement with gases, expertise & know-how, onsite trials, research and development, commercial offers
Contact form for every page
Contact us
select action